How quickly your electric car charges will depend on a variety of different factors. From the size of your electric car battery, to the power output of the charge, and how you charge an electric car considering the state of the vehicle’s maximum charging rate its battery, there’s a lot to be taken into account. Let’s not forget the different types of charges too, ranging from slow to fast to rapid chargers, all of which can affect charging speed.

How long does it take to charge an electric car?
With different types of chargers on the market all ready to charge an electric car, depending on which one or charging method you choose, will determine how long it takes to charge an electric vehicle.
A slow charger has a power output of around 3kW and can take 10 to 14 hours to fully charge an electric car, according to Ovo Energy. These chargers are usually portable and can be plugged into a domestic socket, but they are not recommended for regular use.
A fast charger has a power output of 7kW to 22kW and can take 4 to 6 hours to fully charge an electric car. These chargers are often installed at home or at public places such as supermarkets, car parks, or workplaces.
A rapid charger has a power output of 50kW to 120kW and can take 20 minutes to an hour to charge an electric car up to 80%. These chargers are usually found at motorway service stations and dedicated charging hubs, and they are the fastest way to top up your battery on long journeys.
Some electric vehicles can use ultra-rapid chargers with a power output of up to 350kW, which can give full charge to them in as little as 15 minutes. However, not all electric vehicles are compatible with these chargers, and the charging speed may vary depending on the battery temperature and condition.
How long does it take to charge an electric car at a public charging point?
The time it takes to charge an electric car at a public charging point depends on the type and power of the charger, as well as the size and state of the battery of the car. There are three main types charging speeds of public chargers: slow, fast, and rapid.
However, if you’re looking for an estimate of how long it will take to charge your battery range your electric car at a public charging point, you can use this formula: Battery size (kWh) ÷ Charger power (kW) = Charging time (hours), says ThinkEV.
For example, if you have a Tesla Model 3 Long Range with a 70kWh battery and you use a 50kW rapid charger, it will take, 70 ÷ 50 = 1.4 hours to charge your car from empty to full. However, this is only an approximation, as the charging speed will slow down as the battery gets fuller. Electric vehicles can charge at public charging points and if it’s rapid charging, and your electric vehicle’s battery capacity is decent, your electric car’s battery will be charged before you know it. Public charging stations and car parks are a great place to stop for a quick charge of your battery and can really come in handy. Although you don’t have the worry of having to stop for a charge with a petrol or diesel car, you’ll still need to fill up for fuel and charging an electric vehicle is similar.
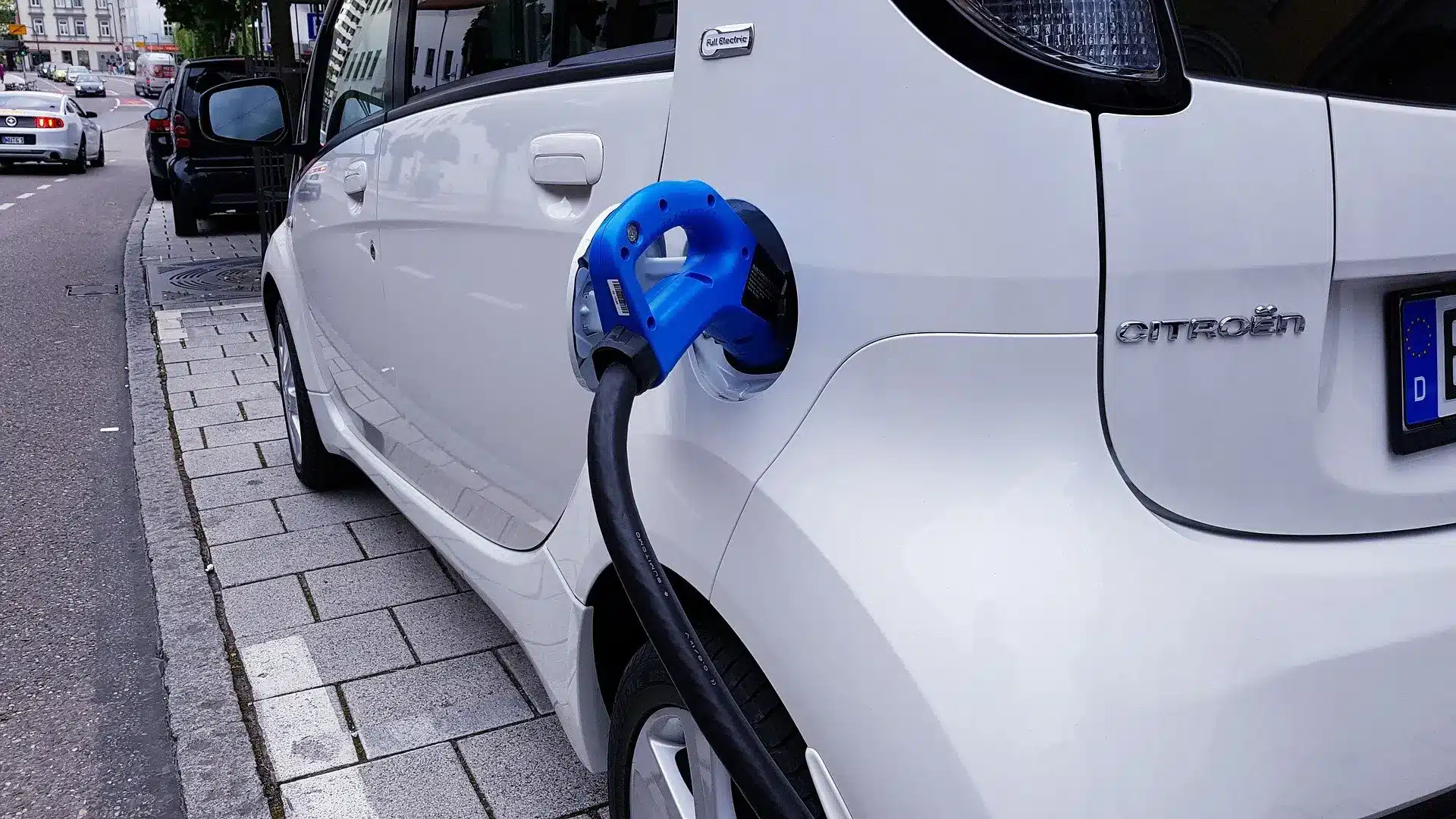

How long does it take to charge an electric car at home?
The time it takes to charge an electric car at home depends on the size of the battery and the power output of the charger. You have two options when charging at home, according to the RAC: using a domestic three-pin plug socket or a dedicated wall box charging station.
A domestic three-pin plug socket has a power output of around 3kW and can take 10 to 14 hours to fully charge an electric car. These chargers are usually portable and can be plugged into a standard outlet, but they are not recommended for regular use, as they are slow and inefficient.
A wall box has a power output of 7kW to 22kW and can take 4 to 6 hours to fully charge an electric car. These chargers are often installed at home or at public places such as supermarkets, car parks, or workplaces. They are faster and safer than using a domestic socket, and they may also qualify for government grants or discounts.
What factors affect EV charging speed?
The speed of charging an electric car can be affected by several factors, such as:
The size and capacity of the battery: The larger the battery, the longer it will take to charge. However, the battery size also determines the range and performance of the electric car, so there is a trade-off between charging speed and driving distance.
The power output of the charger: The higher the power output, the faster the charging speed. However, not all chargers are compatible with all-electric cars, and some chargers may have limited availability or higher costs. There are different types of chargers, such as slow, fast, rapid, and ultra-rapid, with different power outputs ranging from 3kW to 350kW. For example, a 3kW slow charger will take much longer to charge an EV than a 50kW rapid charger.
The state of charge of the battery: The charging speed is not constant throughout the charging process. It tends to be faster when the battery is low and slower when it is full. Most electric vehicles can charge up to 80% in a short time, but the remaining 20% can take much longer. A larger battery will take longer to charge than a smaller one, and a more depleted battery will take longer to charge than a partially charged one, says the RAC.
The temperature and condition of the battery: The optimal temperature range for charging an electric car battery is between 15°C and 35°C. If the temperature is too high or too low, the charging speed may be reduced or interrupted. The battery condition also affects the charging speed, as older or degraded batteries may have lower capacity and efficiency. Extreme temperatures can also affect the battery performance and lifespan.
These are some of the main factors that affect EV charging speed. However, there may be other factors that are specific to certain models or brands of electric vehicles too.
Battery size: How long does an electric car battery last?
The lifespan of an electric car battery depends on various factors, such as the type, quality, usage, and maintenance of the battery. Generally speaking, for most electric cars, car batteries can last for 8 to 10 years or 100,000 to 200,000 miles before they need to be replaced. However, some batteries may last longer or shorter than others, depending on how they are used and cared for.
Some of the factors that can affect the battery life are:
The depth of discharge: The depth of discharge (DoD) is the percentage of the battery capacity that is used before recharging. For example, if a battery has a capacity of 100 kWh and it is used until it has 20 kWh left, then the DoD is 80%. The higher the DoD, the more stress it puts on the battery and the faster it degrades. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid draining the battery completely and to recharge it frequently.
The charging speed: The charging speed is the rate at which the battery is replenished with electricity. The faster the charging speed, the more heat it generates and the more damage it causes to the battery. Therefore, it is advisable to use slow or fast chargers for regular charging and to use rapid or ultra-rapid chargers only when necessary.
The temperature and condition: The temperature and condition of the battery can also affect its performance and longevity. Extreme hot or cold temperatures can reduce the battery capacity and efficiency, as well as increase the risk of overheating or freezing. It is important to keep the battery in a moderate and stable temperature range and to avoid exposing it to direct sunlight or moisture.
The driving style and habits: The driving style and habits of the driver can also influence the battery life. Aggressive driving, such as speeding, accelerating, braking, or cornering hard, can consume more energy and wear out the battery faster. Smooth and steady driving, as well as using eco-mode or regenerative braking, can save energy and extend the battery life.
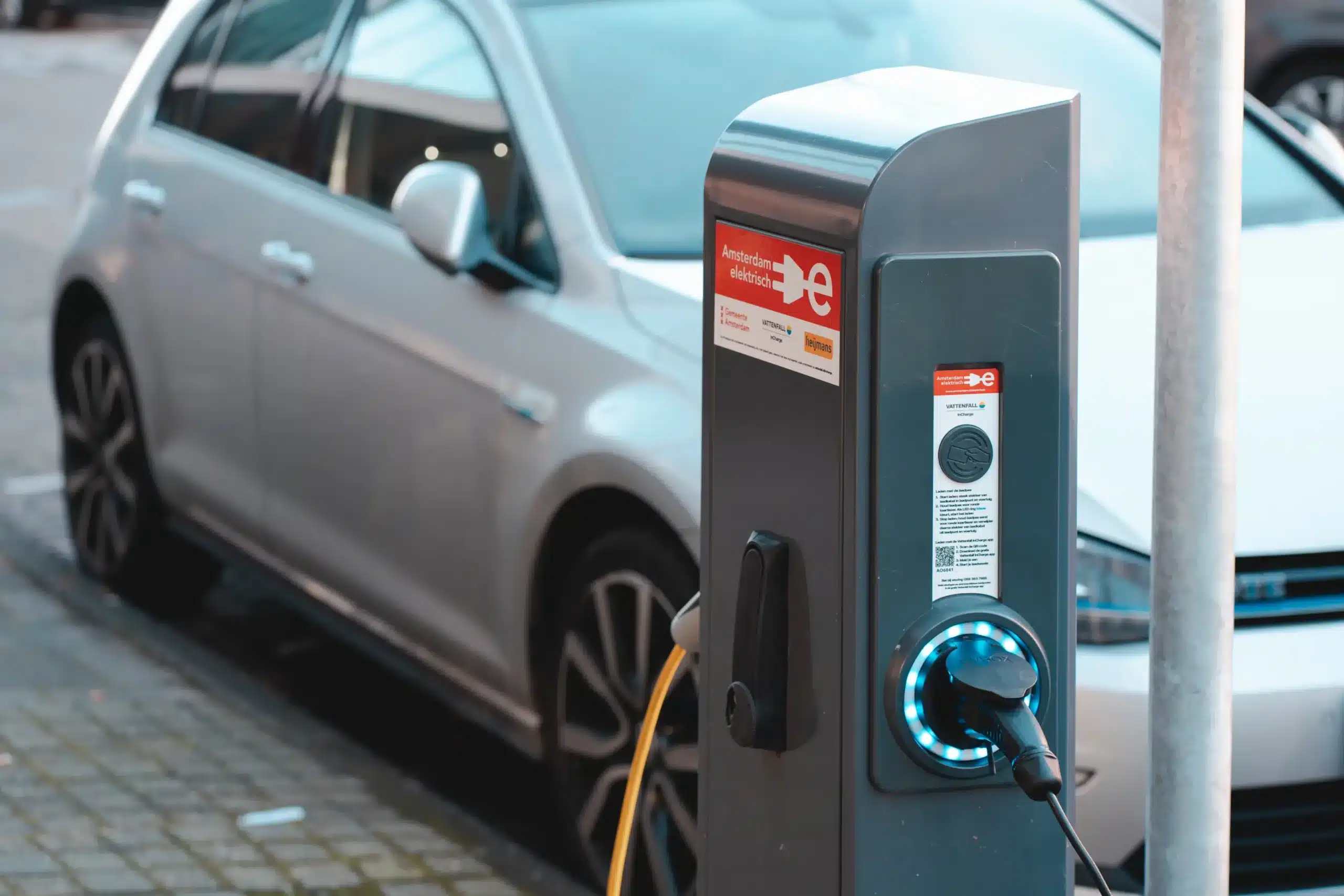

What’s the average charge time for an electric car?
How fast do electric cars really charge? Well, the average charge time for an electric car depends on the size of the battery and the speed of the charging point. According to Eco Cost Savings, it takes 7 hours and 54 minutes to charge an electric car, on average, based on the charge time of 264 electric vehicles. However, this is the combined average for standard, dual and high power charging at 240V. The charge time can vary significantly depending on the electric car charging times, the type of charger and the state of the battery.
Most drivers do not wait for their battery to recharge from empty to full, but rather top up their charge whenever they can. For many electric cars, you can add up to 100 miles of range in about 35 minutes with a 50kW rapid charger, according to Pod Point. Some electric cars, such as Tesla models, can use their own Supercharger network, which can deliver up to 172 miles of range in just 15 minutes, says the RAC.